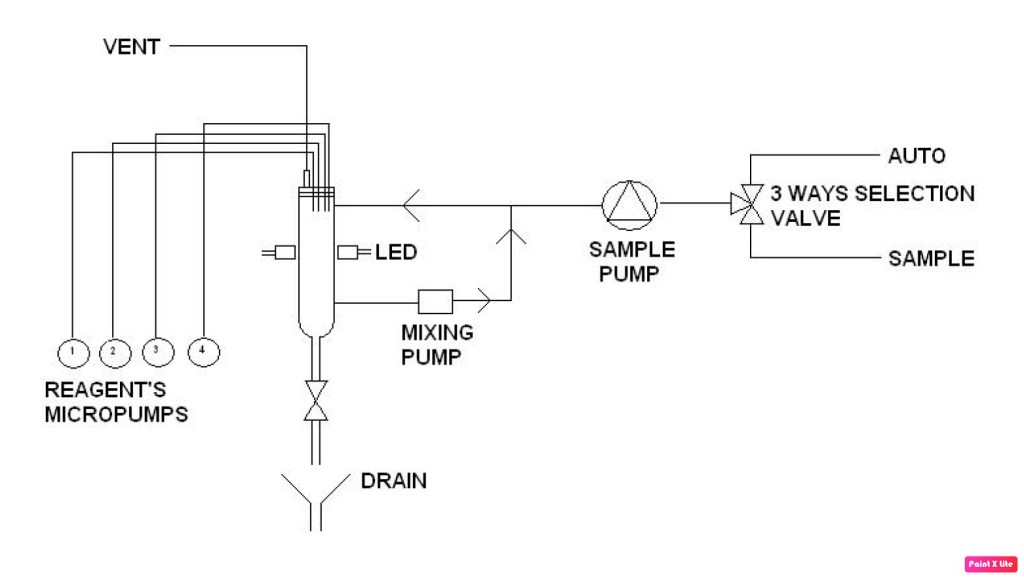
This Colorimeter is a compact analytical instrumentation for online analysis and process monitoring. It is based on a color-developing chemical reaction carried out inside the analyser glass cell. Sample is autonomously grabbed by the instrument and mixed with the appropriate reagents to enable a reaction. The analyser uses an LED light source and a photodiode to photometrically measure the developed color intensity (absorbance). The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of the sample (analyte).
Parameters
Advantages of On-line Analysis:
- Dual compartment enclosure to ensure good separation between electronics and hydraulics.
- Better reliable sampling pump that is able to reach a pump height of up to 5 meters
- Built-in temperature heated controlled reacted measuring cell.
- Quick testing time, average around 7 minutes.
- Good repeatability by automation measurement
- Auto cleaning features that can be programmable
- Interval testing made possible depends on user requirements
- Test on demand available for ad-hoc measurement
- Low reagent level alarm warning.
- Manual datalogging with RS232 download (Standard)
- Connectivity to PLC or wireless network by means of 4-20mA output or RS485 (optional)
- Monitoring of multiple streams (up to 4) possible by multiplexing configuration (built-in feature)
Colorimetric Online Analyser
Applications:
- Waste water treatment plants
- Industrial applications
- Surface water monitoring
- Ultra-pure water
- Steam and condensate water
- Osmosis plants
- Ion exchange systems
- Boiler feed water
- Demineralisers
- Process control
- Process optimisation of waste water treatment plants
- Monitoring of industrial water
- Activated sludge basins
- Waste water treatment plant outlets
- Surface water analysis
- Drinking water analysis
- Industrial water treatments
Aluminium
Aluminium is the most abundant metal and the third most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, behind only oxygen and silicon. It is a lightweight, silvery metal, familiar to every household in the form of pots and pans, beverage cans, and aluminium foil. It is nontoxic, corrosion resistant, non-magnetic, and easy to form or cast into a variety of shapes. It is one of the most useful metals we have.
In spite of the fact that aluminium is very active chemically, it does not corrode in moist air the way iron does. Instead, it quickly forms a thin, hard coating of aluminium oxide. Aluminium is used in water purification because when it reacts with lime (or any base), it forms a sticky precipitate of aluminium hydroxide that sweeps out tiny particles of impurities.
This Colorimeter will measure the aluminium content in water and wastewater.
Chloride
Chloride ions are one of the major inorganic anions in water and wastewater. Although high concentrations of chloride in water are not known to be toxic to humans, its regulation is mainly due to adverse effects on taste. It is essential to monitor chloride concentrations in boiler systems to prevent metal parts from being damaged. In high levels, chloride can corrode stainless steel. The level of chloride concentrations in boiler and cooling towers varies from small quantities to very high levels. Furthermore, high levels of chloride discharge can be toxic to plant life.
Chlorides are the salts of hydrochloric acid with a metal, such as ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), calcium chloride (CaCl2), and magnesium chloride (MgCl2). When dissolved in water, these salts produce chloride ions, Cl-.This Chloride Colorimeter will measure the chloride content in water and wastewater samples.
Chlorine
Chlorine analyser has been developed to check chlorine dosing in disinfection processes with high concentrations of chlorine. The measurement range provided is ideal for the food industry, such as poultry, fruit and vegetable washing.
This Colorimeter will measure the free or total chlorine content in water.
Chromium (VI)
Under normal temperatures, chromium is corrosion-resistant. For this reason, monitoring chromium level plays an important role in the plating industry as well as cooling towers.
Chromium VI is used in textile manufacturing as a catalyst in the dyeing process and as a dye for wool (chrome dyes). Chrome is also the primary threat whenever tanning industry comes into place. Wastes releases from tannery industries contain major toxicity of chromium which releases into the environment direct or indirectly.
Chromium creates unfavorable outcomes by altering the normal physiochemical properties of soil and water.
This Chromium Colorimeter will measure the hexavalent chromium (Cr VI) content in water and wastewater samples.
Copper
Copper is one of the most abundant metals in earth’s crust. Because of its malleability, thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and other useful qualities, it is used in a large variety of industrial and technological applications.
Copper is found in effluents and natural water both as suspended solids and salt. A high concentration is toxic plants and animals, which accounts for its rigorous monitoring by the authorities and industry. Lower concentrations are often employed to contain the growth of plankton and algae.
This Copper Colorimeter will measure the copper content in water and wastewater samples.
Cyanide
Cyanide is a pollutant that originates mostly from metallurgical and galvanic industrial plants. Cyanide is poisonous to the human nervous system, and it is therefore imperative to monitor and control its level in potable water. Continuous monitoring in waste effluents is required, and cyanide is removed using the appropriate procedure.
This Cyanide Colorimeter will measure the cyanide content in wastewater samples.
Hardness
Total hardness refers to the presence of magnesium and calcium and is due mainly to the runoff water dissolving these salts as it flows or filters through different media. Hardness can also be caused by scaling of pipes in cooling and heating systems.
The colorimetric method for measuring hardness is able to measure very low levels of calcium and magnesium. The indicator dye, calmagite, forms a purplish-blue color in a strongly alkaline solution and changes to red when it reacts with calcium and magnesium.
This Hardness Colorimeter will measure the hardness content in water and wastewater samples.
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is a liquid chemical substance normally used in high pressure heating plants because of its properties as an oxygen inhibitor. It is added to avoid scaling and corrosion in the plant itself. Hydrazine reacts with dissolved oxygen to yield nitrogen and water, hydrazine thus has the advantage over the sulfite treatment because it does not produce any dissolved solids in the boiled water. Hydrazine is also used in tanks because it controls the growth of bacteria.
Hydrazine reacts with the p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde to form a yellow color which is proportional to the hydrazine concentration.
This Hydrazine Colorimeter will measure the hydrazine content in water samples.
Iron
Iron is naturally present in water in low concentrations, but it reaches high concentrations in wastewater effluents. The iron concentration in water needs to be monitored because it becomes harmful above certain levels.
In domestic water, iron can be unpleasantly alter the taste, stain laundry, damage kitchenware and favour the growth of certain bacteria. Iron is also an indicator of ongoing corrosion in water cooling and heating systems. And it is normally monitored in mining wastewater to avoid contamination.
This Iron Colorimeter will measure the iron content in water and wastewater samples.
Manganese
Manganese is one of the most common metals present in nature and is used in many industrial applications, for example, the production of fertilizers and in the pharmaceutical industry.
Manganese salts are also used in iron alloys (steel manufacturing) and non-iron alloys as it improves their corrosion resistance and hardness.
This Manganese Colorimeter will measure the manganese content in water and wastewater samples.
Nickel
Nickel is commonly utilized by the electroplating industry in processes, utilising stainless, cobalt or nickel alloys.
Nickel is also used in batteries, fuel cells and hydrogenation of vegetable oils in the food industry.
This Nickel Colorimeter will measure the nickel content in water and wastewater samples.
Nitrite
Nitrites can be harmful to aquatic organisms even in low concentrations and for this reason, they are closely monitored in aquaculture facilities. In cooling towers, however, an adequate amount of nitrites is necessary to prevent corrosion
In high concentrations, they can be harmful to the environmental to the environment and to humans. They are therefore, normally monitored to verify the quality of water for domestic use, as well as lakes and pools.
Nitrites are an intermediate product in the nitrogen cycle and are produced by ammonia oxidation with water, or even originate in industrial waste directly. They must not be present in drinking water.
This Nitrite Colorimeter will measure the nitrite content in water and wastewater samples.
Phosphate
Phosphates are present in a number of products that are used by human everyday.
Phosphates are also extensively used in detergents and cleaning fluids because of their ability to soften water and remove soil deposits.
The largest use of phosphates is in the conversion of the mineral content, which is a mixture of calcium phosphate and other calcium compounds that are used in fertilizers. However, high concentrations of phosphates in agricultural runoff can cause environmental pollution, as they are primary cause of eutrophication.
For these reasons, it is necessary to closely monitor the phosphate levels present in both municipal and industrial wastewater.This Phosphate Colorimeter will measure the phosphate content in water samples.
Silica
Silica is found in all natural waters in the dissolved mineral form. Silica is only slightly soluble in water and therefore depends on the pH level of the water and on the minerals containing silica in contact with water.
Silica’s presence in industrial applications is undesirable since it causes scaling in particular, high pressure turbines are highly affected by this factor. Heating systems and reverse osmosis plants also require monitoring of silica.
This Silica Colorimeter will measure the silica content in water and wastewater samples.
Sulfate
Sulfate is widely present within natural water in different concentrations. Sulfate concentration is to be kept within a strict range for drinking water, especially since this value can be higher as it travels to the consumer pipelines.
Sulfate is also tested in the production of beverages such as beer, due to its significant effect on odor and taste.
This Sulfate Colorimeter will measure the sulfate content in water samples.
Total Phosphorous
Phosphorous is one of the parameter that are beneficial to municipal wastewater treatment customers that need to monitor their biological and chemical nutrient removal process.
Phosphorous is essential nutrients for the plants and animals that make up the aquatic food web, therefore a modest increase in phosphorous can under the right conditions, set off a whole chain of undesirable events in a stream including accelerated plant growth, algae blooms, low dissolved oxygen, and the death of certain fish, and other aquatic aninmals.
This Total Phosphorous Colorimeter will measure the total phosphorous content in water, river and waste water samples.
Zinc
Zinc is normally introduced into drinking water through industrial effluents, especially due to dezincification of brass and deterioration of galvanized iron.
In addition to drinking water, zinc is measured in surface finishing, boilers and cooling towers, and water conditioning and effluent.
This Zinc Colorimeter will measure the zinc content in water and waste water samples.
