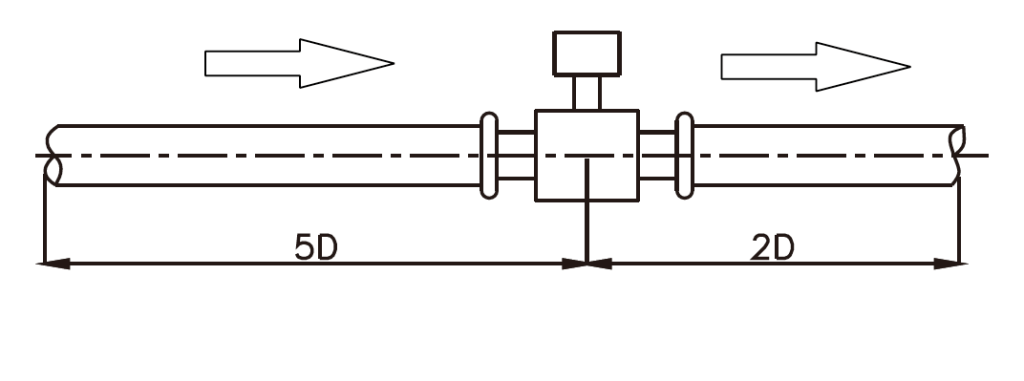
Electromagnetic flow meters detect flow by using Faraday’s Law of induction.
Inside an electromagnetic flow meter, there is an electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field, and electrodes that capture electromotive force(voltage). Due to this, although it may appear as if there is nothing inside the flow pipe of an electromagnetic flow meter, flow can be measured.

Under Faraday’s law of induction, moving conductive liquids inside of a magnetic field generates an electromotive force (voltage) in which the pipe inner diameter, magnetic field strength, and average flow velocity are all proportional. In other words, the flow velocity of liquid moving in a magnetic field is converted into electricity. (E is proportional to V × B × D)
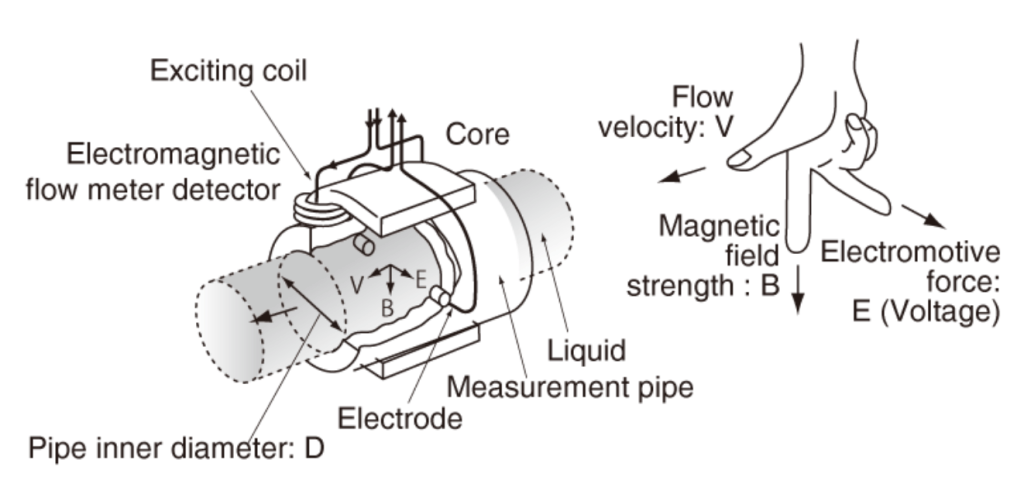
As the flow changes, the electromotive force (voltage) captured by the electrodes changes as follows.
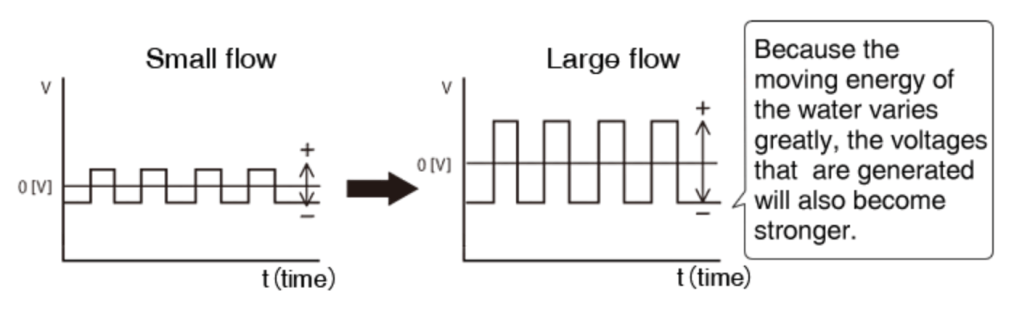
Installation Tips: The straight tube section is required to be at least 5D (internal diameter of the flow meter) on the front side, and at least 2D on the rear side. It is important to note that the pipe must